Regulated environments as medical devices or pharmaceutical sectors requirer the organisations to undergo audits from notify body or competent authorities; ISO organization published the ISO 19011 to define the process and the requirements for management of audits.
In this blog post, we will go through the requirements associated to the audit management process, including principles of auditing, management of audit programme and conjuring management system audits. The last version of ISO 19011 has been published in 2018 and it was prepared by the Project Committee ISO/PC 302.
ISO 19011 : Some Key Definitions
First of all, to start to dive into the ISO 19011, it is very important to provide some key definitions. I will not go through all the definitions provided by the standard, I report here below only the most important ones:
- Audit : systematic documented and independent process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled.
- Audit Programme : Arrangements for a set of one or more audits planned for a specific time frame and directed towards a specific purpose.
- Audit Scope : Extent and boundaries of an audit.
- Audit Plan : Description of the activities and arrangements for an audit.
- Audit Criteria : Set of requirements used as a reference against which objective evidence is compared.
- Audit findings : results of the evaluation of the collected audit evidence against the audit criteria.
- Non-conformity : non-fulfilment of a requirement.
The Different types of Audits
There are three different types of audits and their characteristics can be summarised in the scheme below:
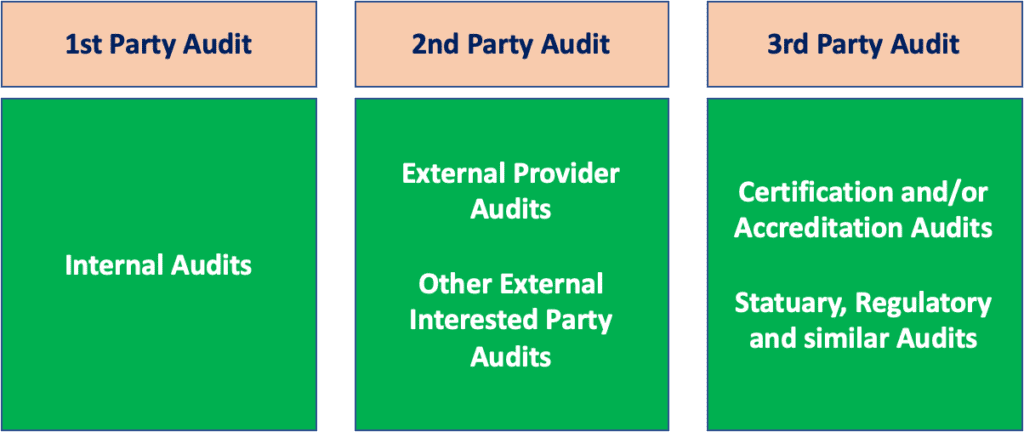
As you can see in the scheme above, we can classify the audits in three categories:
- 1st Party Audits, which are Internal Audits performed by the organization on different processes
- 2nd Party Audits, typically these are supplier audits performed in the framework of vendor assessment / supplier qualification
- 3rd Party Audits, which are inspection performed by competent authorities or by notified body in the framework of certification or accreditation audits, for example for ISO 13485 or ISO 45001 certifications.
The Principles of Auditing according to ISO 19011
The auditing principles according to ISO 19011 can be summarised based on the scheme below:

Let’s briefly discuss about these principles.
Integrity : auditors shall perform their job ethically, with honesty and responsibility. They shall perform their work with the highest impartiality and perform activities for which they are competent.
Fair Presentation : auditors are obliged to report truthfully and accurately. Audit findings, conclusion and reports shall reflect the activities performed during the audits. Obstacles encountered during audits shall be reported, as well as unresolved different opinions with the auditee representative.
Due Professional Care : auditors should display due care aligned with the importance of the task they perform. They should be able to make reasons judgements through all the audit situations.
Confidentiality : auditors should protect confidential information acquired in the course of the audit activities.
Independence : auditors should always be independent from the activities they are auditing. They should not have any conflict of interests. In any case, efforts should be performed in the direction to avoid bias and encourage objectivity.
Evidence-based Approach : audit evidence should be verifiable. In general, an audit shall be based on samples of the information available. An appropriate use of sampling shall be used, which could be dependent from the size of the organization, for example.
Risk-based Approach : a risk based approach shall always be used through the audit. there can be many different situations where a risk-based approach can be used, for example on sampling methods.
The Management of an Audit Programme
According to ISO 19011, the management of the audit programme can be considered in the framework of the Plan – Do – Check – Act. Let’s go through the main steps for the management of an audit programme, taking in considerations the PDCA, which shall always be at the base of any quality process.
Establishing the Audit Programme
In the framework of ISO 19011, the first step in the framework of the management of an audit programme is indeed the establishment of the audit programme. This includes different actives that can be summarised as follows:
- Roles and responsibilities of the person managing the audit programme
- Competence of the person managing the audit programme
- Establishing the extent of the audit programme
- Identifying and evaluating audit programme risks
- Establishing procedures for the audit programme
- Identifying audit programme resources
This planning phase it is essential as it allows to prepare in advance audit operations and to start the audit smoothly in a professional manner. Moreover, it is very important that auditor support the build of a positive collaborative relation with the auditee, in order to make the audit proceed smoothly.
The identification of audit programme resources is also of foundamental importance in the framework of the management of the audit programme. Resources needed for an audit shall be of different categories, for example:
- Financial Resources
- Audit methods
- Availability of auditors
- Technical experts
- Travelling time, cost, accommodation
- Information and communication technologies
Implementing the Audit
The implementation phase for an audit activity consists of the DO phase of the PDCA cycle. The first step of the implementation consists in the definition of audit objective, scope and criteria. Moreover, the audit method shall also be selected. Different audit methodologies can be envisioned, for example:
- Onsite audit, physical presence of the auditor at the site of the organization.
- Remote audit, meaning an assessment through interactive communications.
In order to support the preparation and the activities associated to audits, QualityMedDev published an efficient ISO 13485 Audit Checklist where all the requirements associated to ISO 13485:2016 are listed. This is a tremendous tool that could support your audit process:
Monitoring of an Audit
The monitoring of an audit could correspond to the Check Phase of the PDCA cycle. The following activities shall be performed:
- Evaluate conformity with objectives
- Evaluate audit team members’ performance
- Evaluate audit teams’ ability to implement auditplans
- Evaluate feedback from management
- Take note of changes that impact the auditprogramme
Audit Follow-UP
The outcome of an audit can indicate the need of corrections, or corrective actions or opportunities for improvements. These actions are decided and undertaken by the auditee within the agreed timeframe. The completion and the effectiveness of these actions shall be verified; this verification may be part of a subsequent audit.
Conclusions
In conclusions, we have been describing the main requirements associated to the management of an audit according to ISO 19011. The audit process is composed by different steps that need to be followed for an efficient management of inspections.
QualityMedDev Newsletter
QualityMedDev is an online platform that provides extensive support to medical device manufacturers and consultancy companies in the field of regulatory compliance. We publish blog posts on quality management system and regulatory-related topics and provide extensive documentation ready to be downloaded to support the implementation and maintenance quality system or product-related certifications.
We publish as well a periodic newsletter aimed at sharing information on the new articles or documents which have been made available through QualityMedDev website.
If you would like to stay updated with the last news and analysis from the regulatory world for medical device sector, do subscribe to our newsletter by filling the form below.
Source: https://www.qualitymeddev.com/2021/04/08/iso-19011-guidelines-for-auditing/
- 2016
- accreditation
- activities
- All
- analysis
- articles
- audit
- Blog
- Blog Posts
- body
- build
- care
- Certification
- Communication
- Communications
- Companies
- compliance
- conflict
- Corrections
- Devices
- documents
- First
- form
- Framework
- General
- guidelines
- here
- HTTPS
- Identification
- Impact
- Including
- information
- interactive
- IT
- Job
- Key
- management
- medical
- medical device
- medical devices
- monitoring
- news
- Newsletter
- online
- Operations
- Opinions
- order
- Organisations
- Pharmaceutical
- planning
- platform
- plugin
- Posts
- project
- protect
- publish
- quality
- reasons
- Regulatory Compliance
- report
- Reports
- Requirements
- Resources
- Results
- Risk
- Sectors
- selected
- set
- Size
- start
- stay
- support
- system
- time
- Topics
- Verification
- Website
- within
- WordPress
- Work
- world




